With all the craze and rising awareness surrounding the different cannabinoids, many people are asking what’s the difference between HHC vs THC?
And since we are super passionate about cannabis and hemp and we want our community to be as educated as possible on the topic, we put together this simple guide for you all about HHC vs THC.
and THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) as the focus of the post.
State the purpose: to explore and clarify the differences between these two compounds.
A Brief Background on Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are sticky resinous compounds that affect almost every system in the human body.
They are found in cannabis flowers, leaves, and a few other select plants like hops and cacao.
To learn more about the role of cannabinoids check out our extensive post on all the different types of THC here.
Last time I checked there are over 100 different cannabinoids that have been discovered in the cannabis plant.
All of these cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system and can have various effects.
The most well-known and studied cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), known for its psychoactive properties, and cannabidiol (CBD), which is non-psychoactive and has been researched for its potential therapeutic effects.
However, there are many other cannabinoids, such as CBG (cannabigerol), CBN (cannabinol), and THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin), each with unique properties and potential uses.
The field of cannabinoid research is continually evolving, leading to the discovery and investigation of more compounds within the cannabis plant.
But let’s get back to the point of this article…HHC
What is HHC?
HHC is short for Hexahydrocannabinol. Its chemical structure is slightly different from THC. Not to get all technical on you, but in case you were wondering here’s the structure:
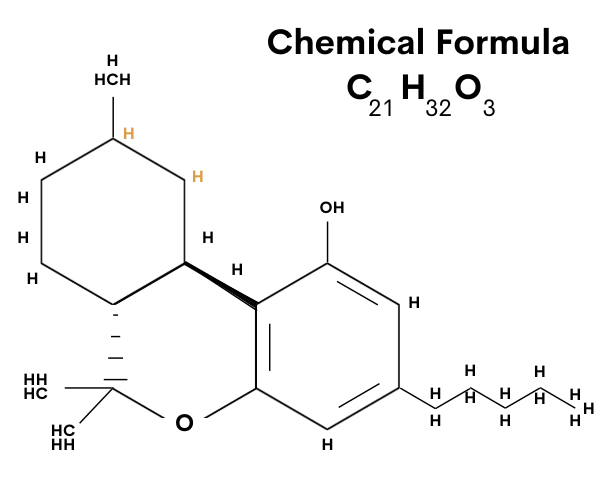
What are the potential effects of HHC?
Although there is very little research and documentation on HHC there are some anecdotal reports that we’ve gotten back from our customers, and from our own experience that we can report on.
What are the effects of HHC?
Some of the potential effects of HHC, just like consuming any cannabis product, could be some of the following:
- Dry Mouth
- Red Eyes
- Anxiety (if overconsumed or not used to consuming cannabinoids)
- Increased Appetite
- Sleepiness or Drowsiness
- Potential Pain-relief
What are the potential benefits of HHC?
When consuming HHC whether smoking it, vaping it, or eating it in edibles, you can expect a more punchy euphoric effect.
We’ve received reports back from customers that it tends to be a little more lightweight compared to straight THC.
- This cannabinoid is great for relaxation, chilling out and just letting go of stress.
- An overall sense of relaxation
So try it out on one of our hemp flower products today and see how you like it!
Current research and legal status of HHC
What is THC?
THC is the most popular, well-known cannabinoid of them all.
It’s a psychoactive cannabinoid and is only found in cannabis.
Although it can be synthesized in a lab. But we don’t recommend that. THC is short for
As you can see the chemical formula for THC is very similar to HHC:
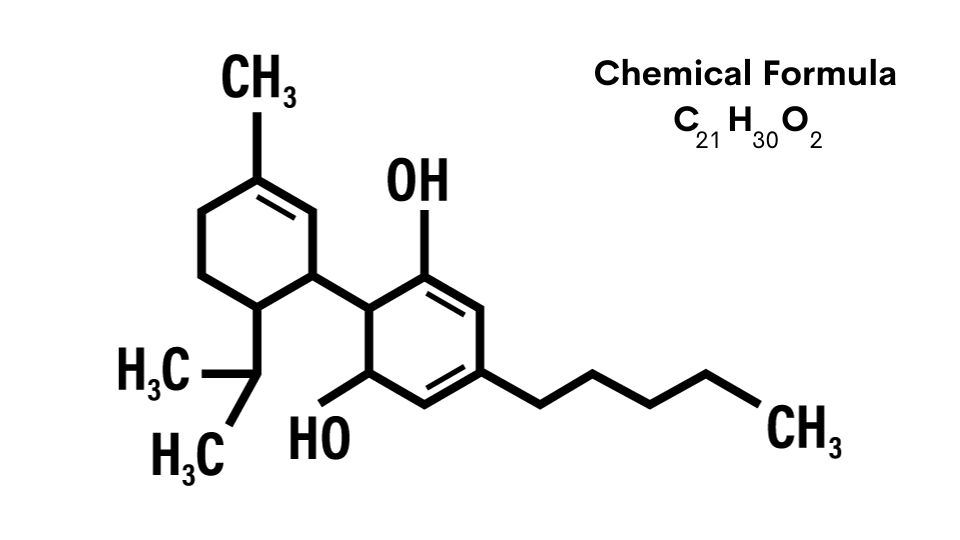
Toward the end of this post we point of a few other key differences between these two chemicals which will be helpful in your studies as well.
What are the Benefits of THC?
The benefits of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), include not only these benefits but here are some of the most popular:
- Pain relief: THC has been found to reduce chronic pain
-
Reduced inflammation: It can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain
-
Improved sleep: THC is associated with changes in slow-wave sleep, which is critical for learning and memory consolidation
- Control of nausea and vomiting: It can control nausea and vomiting caused by cancer chemotherapy
- Improved appetite: THC can stimulate appetite and improve weight gain in people with cancer and AIDS
It’s important to note that while THC offers these potential benefits, it also has side effects and risks, and its use should be carefully considered.

What are the Potential effects of THC?
Being that THC is the most popular and widely used cannabinoid, and, was the first discovered cannabinoid, most people know that this is the famous psychoactive compound that gets you lit.
Depending on how much you consume it will produce different results.
Also, depending on the delivery mechanism and or strain of cannabis it’s being derived from will produce different effects. But some of the most common are:
- Altered Senses: Changes in visual, auditory, and olfactory senses.
- Altered Sense of Time: Many users experience a distortion in their perception of time.
- Mood Changes: THC can cause mood swings, euphoria, or feelings of relaxation.
- Impaired Body Movement: Coordination and motor skills may be affected.
- Cognitive Impairment: Difficulty with memory, thinking, problem-solving, and concentration.
- Increased Heart Rate: Rapid heartbeat can occur shortly after using THC.
- Dry Mouth: Often referred to as “cottonmouth,” users may experience a dry mouth sensation.
- Red Eyes: Bloodshot eyes are a common effect due to dilation of blood vessels.
- Increased Appetite: Commonly known as “the munchies,” where individuals experience heightened hunger.
- Paranoia or Anxiety: Some users may experience feelings of paranoia or increased anxiety.
- Hallucinations and Delusions: High doses of THC can induce hallucinations or delusions, especially in new users or in those with certain mental health conditions.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Users may feel dizzy or lightheaded after THC consumption.
It’s important to note that the severity and occurrence of these side effects can vary depending on the individual, the amount of THC consumed, and the method of consumption.
It’s always advisable to use THC responsibly and be aware of its legal status in your area.
What is THC’s legal status?
Many States in the USA have legalized cannabis consumption, but it is still ironically illegal on a federal level. The federal government has classified the actual cannabinoid THC as a Schedule 1 Drug, not cannabis itself.
This classification allows many companies and individuals to legally consume cannabis with either low levels of THC or cannabis that contains THCa or other psychoactive (or non-psychoactive) cannabinoids.
If you possess or consume THC products on an individual level, you do not need to worry about the federal government coming after you.
However, if you are traveling internationally or crossing any borders, it’s important not to have THC on you.
Transporting large quantities of cannabis with THC in it will raise suspicions of involvement in federally illegal activity.
That’s why ALL the products offered here on the Boston Hemp Inc. website and in our store are THCa-based and contain less than 0.3% THC, which is the legal limit for a cannabis product.
By the way, it is the 0.3% THC content that determines whether a product is classified as hemp or cannabis.

Final thoughts on HHC vs THC
So to summarize the key differences and similarities HHC vs THC we’ve laid out the details in a bullet point format to keep it simple:
HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol):
- HHC is a hydrogenated form of THC.
- It is relatively new in the cannabis market and less researched compared to THC.
- The process of hydrogenation, similar to that used in turning vegetable oil into margarine, is applied to THC to create HHC. This process potentially makes HHC more stable and less susceptible to oxidation.
- The effects of HHC are reported to be similar to THC, including euphoria, altered perception, and potential for pain relief. However, individual experiences may vary.
- There is limited scientific research on HHC, so its full profile of effects and safety is not as well understood as THC.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol):
- THC is the primary psychoactive component of the cannabis plant.
- It is well-researched and known for producing effects such as euphoria, relaxation, altered senses, and, in some cases, anxiety or paranoia.
- THC binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and body, leading to its psychoactive effects.
- It is used both recreationally and medicinally, with applications in pain relief, appetite stimulation, and managing conditions like glaucoma and PTSD.
- THC is a controlled substance in many regions, with varying legal statuses depending on the country or state.
Similarities:
- Both HHC and THC are compounds derived from the cannabis plant.
- They share psychoactive properties and can induce effects like euphoria and altered perception.
- Both are used in similar product forms, such as edibles, vapes, and oils.
Differences:
- HHC is a hydrogenated derivative of THC and is less researched.
- The legal status of HHC might differ from THC, as it is a newer compound and may not be explicitly regulated in some regions.
- The safety profile and full spectrum of effects of HHC are less understood compared to THC.
It’s important to note that the effects and legal status of these compounds can vary significantly based on the individual and jurisdiction.
Research & Investigation into HHC vs THC
Further research and consultation with healthcare professionals are advisable for anyone considering the use of these substances.
The potential of HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) and THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) in the future of cannabinoid research and therapy is an intriguing topic, especially given the rapidly evolving landscape of cannabis science and its applications in therapeutic contexts.
Let’s delve into their potential roles as it relates to research:
HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol)
- Exploration of Novel Cannabinoids: HHC, as a hydrogenated form of THC, represents a growing interest in exploring novel cannabinoids beyond the well-known THC and CBD. This exploration could lead to a broader understanding of the therapeutic potential of lesser-known cannabinoids.
- Chemical Stability: The hydrogenation process that creates HHC potentially imparts greater stability to the molecule, which could be beneficial in pharmaceutical formulations, leading to longer shelf life and potentially more consistent therapeutic effects.
- Legal and Regulatory Opportunities: Given HHC’s relative novelty, it currently occupies a less defined space in terms of legal and regulatory status. This could allow for more flexibility in research and development, at least in the short term, potentially fast-tracking studies and clinical trials.
- Psychoactive Properties and Safety Profile: Understanding HHC’s psychoactive effects and safety profile is crucial. If HHC demonstrates a favorable safety profile with less intense psychoactive effects compared to THC, it could become a preferred option for certain therapeutic applications.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Expanding Therapeutic Applications: THC is well-recognized for its psychoactive effects, but its therapeutic potential in pain management, appetite stimulation, and as an antiemetic is increasingly acknowledged. Ongoing research may uncover more nuanced therapeutic uses, including potential neuroprotective properties.
- Personalized Medicine: The variability in individual responses to THC suggests a potential role in personalized medicine. By understanding genetic and biochemical factors that influence these responses, THC-based treatments could be more effectively tailored to individual patients.
- Combination Therapies: THC’s efficacy might be enhanced when used in combination with other cannabinoids (like CBD) or traditional pharmaceuticals. This synergy could pave the way for novel combination therapies for various conditions.
- Psychological and Neurological Research: THC is a valuable tool in researching brain function and psychological disorders. Its impact on the brain’s endocannabinoid system can provide insights into the treatment of conditions like PTSD, anxiety disorders, and even certain addictions.
General Prospects in Cannabinoid Research and Therapy
- Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Innovations in drug delivery systems, such as nanoemulsions and transdermal patches, could improve the efficacy and reduce side effects of HHC and THC, making them more viable in therapeutic settings.
- Regulatory Evolution: As the legal landscape around cannabis continues to shift, there may be more opportunities for research and clinical use of cannabinoids like HHC and THC. This could lead to more comprehensive studies and broader acceptance in medical practice.
- Understanding Long-term Effects: Long-term studies on the effects of HHC and THC are essential for understanding their impacts on health, which is critical for their therapeutic use.
- Educational and Social Change: As research progresses, educating healthcare professionals and the public about the benefits and risks of cannabinoids will be key. This will help in destigmatizing their use and integrating them more fully into healthcare systems.
In summary, the future of HHC and THC in cannabinoid research and therapy is promising, marked by potential innovations in treatment strategies and a deeper understanding of their effects.
The path forward will likely involve a combination of scientific exploration, regulatory changes, and a shift in societal perceptions regarding cannabis and its derivatives.
References/Further Reading on HHC vs THC
Scientific studies, legal resources, or educational materials to explore more:
- https://www.jwu.edu/news/2021/09/7-potential-health-benefits-of-cannabis.html
- https://www.forbes.com/health/cbd/health-benefits-of-cannabis/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK425767/
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/medical-marijuana-faq